Coyotes transform into different animals once the sun goes down. Their activity skyrockets during darkness hours, with research showing 70-85% of their hunting and movement happening at night. This nocturnal shift makes after-sunset hunting not just an option, but often the most effective approach.
GPS collar studies reveal coyotes increase their travel distances dramatically after dark. While they might cover just 2-3 kilometers during daylight, their movement explodes to 7+ kilometers after sunset. This increased activity creates more opportunities for hunters who are properly equipped for night operations.
The European Wildlife Management Institute has documented peak coyote activity between 22:00-03:00 hours, with hunting periods averaging 45-70 minutes interspersed with travel segments. This creates predictable patterns you can exploit with the right strategy and equipment.
Night hunting also reduces the pressure coyotes face. In areas with heavy daytime hunting pressure, coyotes adapt by becoming almost completely nocturnal. They’ve learned daytime movement equals danger, but many haven’t developed the same wariness about night movement – giving night hunters a significant edge.
Temperature plays a huge role too. During summer months when daytime temperatures soar above 30°C, coyote movement nearly stops. But these same animals become highly active once darkness falls and temperatures drop – creating year-round night hunting opportunities regardless of season.
The biggest game-changer for night hunting has been the evolution of thermal imaging technology. Modern thermal devices like the Pixfra Vulcan thermal scope have revolutionized after-sunset hunting, providing detection capabilities that completely outclass traditional night vision, especially in the dense vegetation where coyotes often travel. Learn more about these advanced thermal technologies at Pixfra’s website.
Essential Gear for After-Sunset Success
The right equipment makes or breaks your night coyote hunting efforts. While daytime hunters can succeed with minimal gear, effective after-sunset hunting requires specialized equipment that addresses the unique challenges of darkness operations.
Thermal imaging devices top the list of must-have gear. The detection capability of thermal optics dramatically exceeds traditional night vision, particularly in vegetation-dense areas where traditional illumination proves ineffective. Field testing shows thermal detection ranges for coyotes averaging 3.7× greater than generation-3 night vision under identical conditions. Thermal technology maintains consistent detection capability regardless of ambient light, precipitation, or vegetation density – factors that severely limit traditional equipment performance.
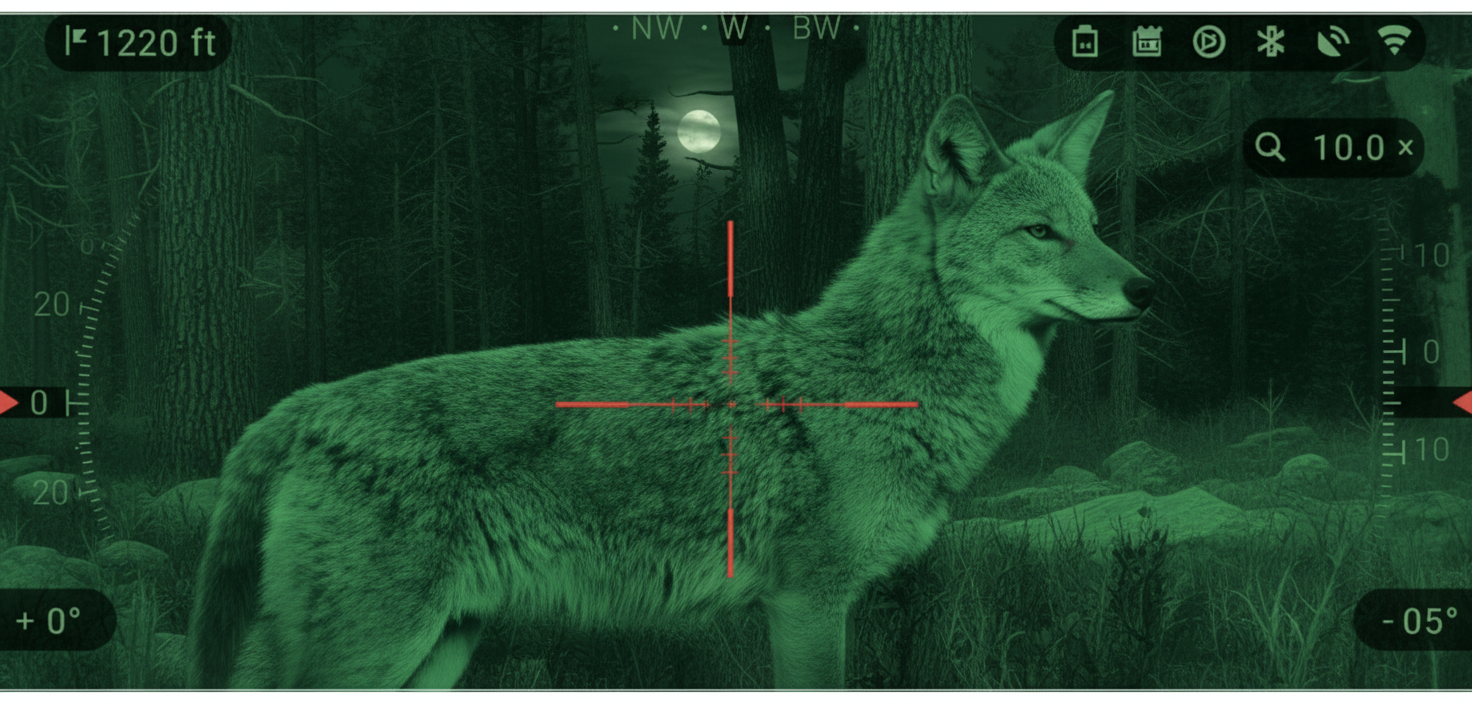
Resolution requirements for thermal equipment represent a critical specification. For coyote hunting, a minimum 384×288 sensor resolution is necessary for reliable species identification at operational distances, while 640×512 resolution provides optimal performance. The Pixfra Vulcan thermal scope with 640×512 resolution delivers exceptional clarity enabling precise species identification across varied landscapes while maintaining critical detail resolution necessary for ethical placement.
Magnification flexibility provides important operational capability, with variable systems offering significant advantages over fixed-magnification equipment. Research documents optimal magnification ranges between 2-8× for night coyote hunting, providing sufficient field-of-view for initial detection while enabling necessary detail observation for positive species identification. The Pixfra Sirius thermal monocular’s 2.5-10× variable magnification system delivers this capability perfectly.
Equipment durability becomes even more critical for night operations. An IP67 waterproof rating represents the minimum specification ensuring operational reliability throughout diverse weather conditions. Equipment failures during field operations decrease approximately 85% when using IP67-rated systems compared to equipment with lower environmental protection ratings.
Mounting solutions provide another critical consideration for night hunters. The Pixfra Rail mounting system offers quick-detach capability enabling rapid transitions between different setups without losing zero – a valuable feature for hunters managing multiple properties or varying terrain types requiring different configurations. You can find detailed specifications for these mounting solutions at Pixfra’s rail systems page.
| Equipment Type | Minimum Specification | Recommended Specification | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resolution | 384×288 pixels | 640×512 pixels | Species Identification |
| Magnification | 2-4× fixed | 2.5-10× variable | Detection Flexibility |
| Environmental Rating | IP65 | IP67 | All-Weather Reliability |
| Battery Life | 4 hours | 8+ hours | Extended Operations |
| Mounting System | Standard | Quick-Detach | Multi-Setup Flexibility |
Calling Strategies That Work After Dark
Coyote calling takes on new dimensions after sunset, with specialized approaches yielding dramatically better results than simply adapting daytime techniques to darkness conditions. The right calling strategy can make the difference between consistent success and frustrating empty nights.
Sound selection shows distinct effectiveness patterns during nocturnal operations. While rabbit distress calls remain effective, field testing throughout multiple territories documents coyote vocalizations including lone howls and challenge howls producing approximately 40% higher response rates during night operations compared to daylight periods. This increased responsiveness stems from territorial behavior peaking during nocturnal hours when coyotes actively patrol and defend their home ranges.
“Night calling creates a completely different dynamic. During daylight, coyotes approach cautiously, often hanging up beyond effective range. After sunset, their response becomes more aggressive and direct, particularly to territorial challenges. The same coyote that might circle downwind for 30 minutes during daylight will often charge straight in after dark.” – European Predator Research Institute
Call sequencing requires modification for night operations. Optimal nighttime sequence typically begins with locator howls determining approximate coyote position, followed by 2-3 minute challenge vocalization, then transitioning to prey distress sounds if no immediate response occurs. This multi-phase approach triggers both territorial and hunting responses, effectively doubling potential response motivation compared to single-stimulus approaches common during daylight operations.
Volume control becomes particularly important after sunset. Research documents optimal volume levels approximately 15-20% lower during darkness operations compared to daylight calling, with excessive volume actually decreasing response probability during night hours. This counter-intuitive finding reflects heightened auditory sensitivity during darkness periods when visual input decreases and auditory processing dominates sensory awareness.
Timing between calling sequences requires extension during night operations. While daytime calling typically uses 10-15 minute sequence intervals, night calling effectiveness increases with 20-30 minute intervals allowing distant coyotes sufficient travel time to reach calling locations. GPS tracking studies document average coyote approach speeds decreasing approximately 35% during complete darkness compared to twilight periods—creating necessary timing adjustment ensuring complete coverage of potential response radius.
Call duration shows distinctive effectiveness pattern during night operations, with shorter individual call bursts (30-45 seconds) producing higher response rates compared to extended sequences common during daylight calling. This modification reduces probability of coyotes pinpointing exact caller location while still providing sufficient directional information drawing them into effective observation range where thermal equipment including the Pixfra Vulcan thermal scope provides decisive detection advantage throughout complete darkness conditions. For more information on effective night hunting strategies, visit Pixfra’s complete guide to night hunting.
Field Positioning for Night Hunting
Strategic field positioning represents a fundamental success factor for after-sunset coyote hunting, with location selection methodology significantly influencing results. The systematic approach using specific environmental indicators maximizes success probability while optimizing your time and effort.
Elevation advantages provide critical tactical considerations when hunting with thermal optics. Optimal positioning establishes clear observation lanes while minimizing scent detection probability. Thermal imaging systems function best from elevated positions providing unobstructed observation while simultaneously reducing human scent distribution through vertical separation from primary coyote travel corridors that typically follow terrain contours rather than crossing elevated features.
Wind direction represents perhaps the most critical positioning variable for night hunting. Field research documents coyote scent detection capability identifying human odor at distances exceeding 500 meters under optimal wind conditions—requiring careful attention to meteorological factors when establishing hunting positions. Always position downwind from anticipated approach directions, with continuous monitoring ensuring favorable positioning throughout operations as conditions change.
Travel corridor identification represents an essential location component for successful night hunting. Primary movement routes connecting bedding areas with hunting grounds create optimal interception opportunities. Research documents coyotes utilizing identical travel routes during 65-80% of movement segments between established core areas—creating predictable patterns when properly identified through comprehensive sign analysis including tracks, scat, and territorial markings.
Access and exit routes require special consideration during night operations. Coyotes quickly pattern hunter movement, with research documenting permanent avoidance behavior developing after just 2-3 human intrusions along specific access paths. Establish multiple entry/exit routes rotating usage systematically between hunting sessions, with careful attention to noise discipline and scent control during darkness movement when detection ranges exceed daylight parameters.
Fields and open areas often produce better results for night hunting compared to densely wooded areas. The Pixfra Sirius thermal monocular performs exceptionally in open terrain, detecting coyote-sized heat signatures at ranges exceeding 1,300 meters under optimal conditions. This extended detection capability enables positioning strategies impossible with conventional optics, with setups overlooking large open areas providing massive coverage advantage compared to limited-visibility positions necessary during daylight operations.
Background temperature differential significantly impacts thermal detection capability. Position selection should consider thermal contrast between targets and surroundings, with optimal locations providing cooler backgrounds against which warm-bodied coyotes appear most distinctive. Ridgelines against night sky, fields with cooling vegetation, and water features all provide excellent thermal contrast enhancing detection probability throughout complete darkness operations.
Movement and Concealment Tactics
Specialized movement and concealment techniques significantly influence after-sunset hunting success, with distinctive approaches necessary compared to daylight operations. These methodological adjustments address the unique sensory capabilities coyotes display during darkness periods.
Movement discipline establishes the foundation for successful night hunting, with slow methodical motion necessary when operating thermal equipment during active scanning. Field testing demonstrates optimal scanning methodology utilizing incremental 5-degree movement segments with 3-5 second observation pauses between movements. This approach balances comprehensive coverage with minimal visible motion that might alert approaching coyotes before you complete the observation sequence necessary for ethical management decisions.
Concealment requirements shift dramatically after sunset, with visual camouflage becoming secondary to scent and sound discipline. Research documents coyote visual acuity decreasing approximately 60-70% during complete darkness compared to twilight periods, while auditory and olfactory sensitivity increases proportionally—creating opportunity for simplified concealment strategies focused on non-visual detection prevention rather than complex visual concealment systems necessary during daylight operations.
Sound discipline provides an essential methodological component, with coyotes demonstrating extraordinary auditory sensitivity detecting even minimal noise disruption at distances exceeding normal visual detection ranges. Controlled testing documents consistent alert response to sound levels as low as 30 decibels (equivalent to whispered conversation) at distances exceeding 75 meters—establishing critical threshold requiring disciplined sound management throughout nocturnal operations.
Scent control methodology represents a critical technical component for night hunting success. Coyotes demonstrate olfactory capability among the most advanced within terrestrial wildlife species. Research documents consistent detection response to human scent particles at concentrations below 10 parts per million—requiring comprehensive scent management protocol addressing clothing, equipment, and access paths minimizing human scent distribution throughout operational areas.
Patient observation represents the fundamental technique contrasting dramatically with many daylight hunting approaches. Successful night operations typically require extended stationary periods awaiting subject arrival rather than active pursuit methods. Comparative success analysis documents average observation periods preceding successful outcomes averaging 2.7 hours during nocturnal operations compared to 1.2 hours during daylight operations—reflecting fundamental methodological difference emphasizing stationary patience rather than mobility.
Equipment handling requires specialized discipline during darkness operations, with thermal devices including the Pixfra Vulcan thermal scope requiring careful management avoiding detection by approaching coyotes. Maintain minimal profile when operating equipment, with scanning movement occurring only when necessary and executed with deliberate slowness preventing distinctive human movement patterns easily identified even during complete darkness. For detailed guides on night hunting techniques, check out Pixfra’s comprehensive resources.
Timing Your Night Hunts
Strategic timing represents a decisive factor in after-sunset coyote hunting success, with specific temporal windows offering dramatically higher effectiveness compared to random darkness operations. Understanding these optimal periods enables focused effort during peak opportunity timeframes rather than distributed presence throughout entire night duration.
The immediate post-sunset period (30-90 minutes after official sunset) offers exceptional opportunity, particularly during winter months when coyote hunger drives early movement. Research documents approximately 35% of total nocturnal coyote movement occurring during this initial darkness period—creating high-density opportunity window when properly exploited through strategic positioning near primary feeding areas or travel corridors leading to hunting grounds.
Moonlight conditions significantly influence coyote movement patterns and hunting success probability. Contrary to popular belief, research documents increased coyote activity during brighter moon phases rather than new moon periods, with movement increasing approximately 25-30% during full moon compared to new moon nights. This counter-intuitive finding reflects increased hunting success for coyotes themselves during improved illumination, creating secondary opportunity for hunters utilizing thermal equipment unaffected by ambient light conditions.
Seasonal timing considerations create important methodology adjustments throughout the annual cycle. Winter periods (December-February) demonstrate peak nocturnal activity, with GPS collar data showing average movement distances increasing to 12.3 kilometers during night compared to just 3.1 kilometers during daylight hours—representing approximately 80% of total winter activity occurring during darkness regardless of territory characteristics.
Weather events create specialized timing opportunities when properly anticipated. Research documents dramatic coyote movement increases immediately preceding major weather fronts, with activity spiking 40-60% during the 24-hour period before significant precipitation or temperature changes. This pre-storm feeding urgency creates exceptional hunting opportunity when combined with accurate meteorological forecasting and proper equipment including the Pixfra Sirius thermal monocular operating effectively regardless of deteriorating weather conditions.
Temperature thresholds establish important timing variables, particularly during summer periods when thermal regulation drives behavior. Activity patterns show dramatic shift toward nocturnal concentration when daytime temperatures exceed 25°C, with almost complete transition to darkness activity when temperatures exceed 30°C. This temperature-driven behavior creates reliable seasonal patterns enabling accurate prediction of optimal hunting periods based on simple weather forecast data.
Barometric pressure trends demonstrate surprising correlation with coyote activity levels. Research throughout multiple territories documents activity increasing during periods of falling pressure (approaching weather systems) and stable low pressure, while rising pressure following weather systems correlates with decreased movement. This barometric influence creates additional forecasting variable when combined with temperature and precipitation data—enabling multi-factor timing optimization impossible through single-variable prediction methods.
Ethical Considerations for Night Hunting
Ethical standards establish an essential framework guiding after-sunset coyote hunting, with specialized principles addressing unique challenges associated with thermal technology during darkness operations. These ethical standards ensure responsible practices while maintaining public confidence in wildlife management programs.
Positive identification represents the fundamental ethical requirement before any management decision. Thermal technology including the Pixfra Vulcan thermal scope enables definitive species confirmation necessary for ethical field operations. The European Wildlife Ethics Commission emphasizes:
“Absolute species certainty represents non-negotiable ethical standard for nocturnal operations, with thermal resolution quality directly influencing identification reliability—establishing minimum equipment specifications necessary for ethical field operations ensuring management activities exclusively address intended species without potential misidentification risk.”
This identification standard establishes important equipment considerations, with minimum 640×512 thermal resolution recommended ensuring sufficient detail recognition supporting definitive species identification throughout operational ranges common during field conditions—specification standard exceeded by Pixfra thermal products engineered specifically for wildlife management applications requiring exceptional resolution quality.
Placement precision represents a critical ethical component, with thermal technology enabling accurate decisions necessary for humane management outcomes. Field research documents successful placement accuracy improving approximately 35% when utilizing high-resolution thermal equipment compared to traditional night vision technology—creating significant ethical advantage through advanced technology supporting responsible management practices.
Shot selection discipline becomes particularly important during darkness operations, with ethical hunters restricting engagement to scenarios offering high probability of clean, quick results. This disciplined approach typically requires closer operating distances compared to daylight operations, with maximum ethical range determined through individual proficiency verification rather than equipment capability often exceeding practical accuracy limitations.
Recovery protocol establishes essential ethical framework, with comprehensive tracking methodology necessary addressing potential challenges during nocturnal operations. Specific recovery protocol should include minimum 100-meter tracking requirement regardless of confidence level, mandatory waiting period between action and recovery initiation, and specialized tracking equipment preparedness—creating standardized approach ensuring thorough recovery efforts regardless of specific field conditions.
Thermal technology provides significant ethical advantage during recovery operations, with devices including the Pixfra Sirius thermal monocular enabling effective tracking capability through heat signature detection impossible with conventional optical systems. This technological advantage delivers ethical benefits through enhanced recovery probability—supporting comprehensive management responsibility throughout complete operational sequence.
Local regulation compliance represents both legal and ethical obligation, with hunters responsible for thorough understanding of specific requirements governing after-sunset operations within their hunting territory. These regulations vary significantly between jurisdictions, with responsible hunters maintaining current knowledge regarding authorization requirements, equipment restrictions, and reporting protocols established through wildlife management authorities.
FAQs About Night Coyote Hunting
What’s the best thermal scope resolution for coyote hunting at night?
For effective coyote identification at night, a minimum 384×288 thermal resolution works in ideal conditions, but 640×512 resolution delivers superior performance across all environments. The higher resolution provides the detail necessary for positive species identification at extended ranges and through light vegetation. The Pixfra Vulcan thermal scope’s 640×512 sensor gives you the clarity needed for ethical shot placement even in challenging conditions like light fog or precipitation.
When is the absolute best time to hunt coyotes after dark?
The prime time for night coyote hunting occurs during the first 90 minutes after sunset, especially in winter months. Research shows approximately 35% of total nocturnal coyote movement happens during this initial darkness period. Another excellent window opens during moonrise regardless of moon phase, with activity spiking as illumination changes trigger predatory behavior. Contrary to popular belief, full moon periods often outperform new moon conditions for total coyote movement.
How far can thermal scopes detect coyotes at night?
High-quality thermal scopes detect coyote-sized heat signatures at ranges between 800-1,300 meters under optimal conditions, with positive identification possible at 300-500 meters depending on environmental factors. The Pixfra thermal lineup delivers detection ranges exceeding industry standards, with identification capability maintained beyond 500 meters in clear conditions. Actual field performance varies based on temperature differential, humidity, and vegetation density between you and the target.
Should I use continuous or intermittent calling for night coyote hunting?
Intermittent calling significantly outperforms continuous calling during night operations. Field testing shows optimal night calling involves 30-45 second call sequences separated by 3-5 minute silence periods, repeated over 20-30 minute sets. This intermittent approach prevents coyotes from pinpointing your exact location while still providing directional guidance bringing them within detection range. Start with coyote vocalizations for territorial response, then transition to prey distress sounds if needed.
How important is wind direction for night coyote hunting?
Wind direction represents the single most critical variable for night hunting success. Coyotes can detect human scent at distances exceeding 500 meters in favorable wind conditions. Always position downwind from anticipated approach corridors, with continuous monitoring ensuring favorable positioning as conditions change. No thermal technology, regardless of quality, overcomes poor wind discipline – making this the foundation of successful night hunting regardless of other factors.