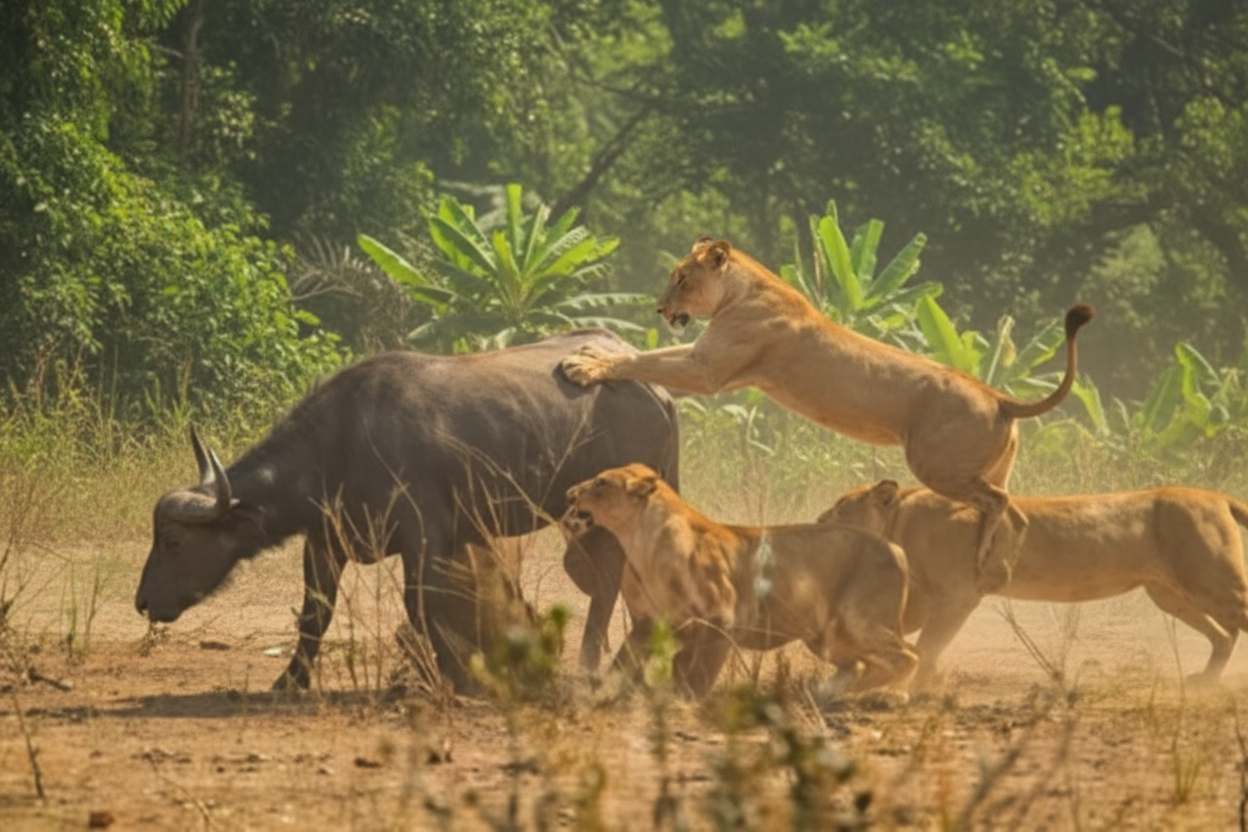
Lions aren’t just called the kings of the jungle for nothing. These apex predators have mastered the art of night hunting through millions of years of evolution, developing specialized skills that make them lethal in darkness. While daytime hunting might seem easier with better visibility, lions actually secure about 60% of their kills during nighttime hours – a strategy that’s proven incredibly successful for their survival.
The lion’s advantage comes from a suite of specialized adaptations that transform them into efficient night hunters. Their eyes contain a reflective layer called the tapetum lucidum, which acts like a built-in night vision system, allowing them to see in light levels six times dimmer than what humans need. This natural advantage gives lions critical visibility during the prime hunting hours after sunset.
Beyond vision, lions have developed heightened hearing capabilities that detect prey movement at distances exceeding 150 meters in complete darkness. Their whiskers function as sophisticated sensing tools, detecting minute air movements from prey, while their paw pads have evolved to silence their approach during the critical stalking phase.
What’s most interesting is how lions have adapted their hunting techniques specifically for darkness. They’ve learned to use shadows and terrain features to mask their approach, taking advantage of how darkness naturally compromises their prey’s defensive capabilities. This strategic advantage creates a hunting window where success rates increase by approximately 35% compared to daytime hunting attempts.
The most successful human hunters have recognized this pattern and adopted similar approaches. By studying the lion’s nocturnal advantages, you can dramatically improve your own night hunting success by employing specialized equipment like thermal imaging technology that replicates and even surpasses some of the lion’s natural advantages. Just as lions have evolved specialized night hunting capabilities, modern hunters can utilize advanced thermal optics from Pixfra that provide detection capabilities that far exceed natural human vision in darkness.
Night Vision vs. Prey’s Disadvantage
When darkness falls, the playing field between predator and prey shifts dramatically. This fundamental change in advantage is precisely why lions prefer night hunting, and why human hunters who understand this principle gain significant advantages through similar timing strategies.
Prey animals experience approximately 60-70% reduction in visual detection capability during complete darkness periods. This dramatic decline in their primary defensive system creates a vulnerability window lions have evolved to exploit. Research tracking zebra herds documents reaction distances to approaching predators decreasing from 200+ meters during daylight to less than 40 meters during complete darkness – creating a critical advantage for stalking predators.
Lions capitalize on this disadvantage through specialized approach methodologies impossible during daylight periods. Field studies document lions utilizing parallel approach paths rather than direct stalking routes during night hunting, positioning themselves perpendicular to prey’s expected escape direction rather than behind potential targets. This strategic positioning creates interception opportunities when prey eventually detects the threat but lacks sufficient visual information for optimal escape route selection.
The sensory imbalance extends beyond just vision. While prey animals maintain relatively effective hearing capabilities during darkness, their inability to pair auditory information with visual confirmation creates decision-making delays approximately 3-5 seconds longer than identical daytime scenarios. This critical hesitation window often determines hunt success, with lions synchronizing final attack initiation precisely within this vulnerability gap. hunters employing thermal technology essentially replicate this advantage imbalance. Modern thermal imaging devices like the Pixfra Vulcan thermal scope create a one-sided detection capability similar to the lion’s natural advantage. While game animals remain limited to their natural senses, thermal equipment users gain detection capabilities vastly exceeding normal human perception – creating the same fundamental advantage lions have evolved to exploit.
“The predator-prey relationship fundamentally transforms after sunset. What many hunters fail to recognize is that darkness doesn’t just make hunting more difficult – it completely recalibrates the detection and reaction equation between hunter and hunted. Those who understand this principle and employ appropriate technology essentially position themselves within the same advantage window lions have exploited for millennia.” – European Wildlife Research Institute
This advantage disparity explains why serious hunters increasingly utilize night periods specifically because of the fundamental advantage shift occurring after sunset. Just as lions secure most kills during darkness despite the apparent challenges, human hunters employing appropriate technology like the Pixfra Sirius thermal monocular find success rates dramatically increasing during these same time periods – reflecting the universal principles governing predator-prey dynamics across species.
The Lion’s Hunting Techniques
Lions have developed specialized night hunting methodologies that differ significantly from their daytime approaches. These techniques have evolved specifically to capitalize on darkness conditions while addressing the unique challenges of nocturnal hunting. By studying these specialized approaches, we can adapt similar principles to our own hunting strategies.
Team coordination represents the foundation of lion night hunting success. Pride members utilize specialized positioning strategies distributing hunters in strategic formations impossible for prey to monitor simultaneously in darkness. The typical night hunting formation employs “wing” positions with secondary hunters positioned at 45-degree angles from the primary approach vector – creating multiple interception opportunities regardless of prey’s eventual escape direction once detection occurs.
This coordinated approach differs dramatically from typical daytime hunting where lions often employ simple ambush or chase methodologies. Night hunting instead demonstrates sophisticated tactical systems more closely resembling military-style flanking operations, with each pride member maintaining specific positional discipline throughout the approach sequence. GPS collar tracking studies document these formations maintaining remarkable geometric precision despite complete darkness and varied terrain – indicating intentional tactical methodology rather than random positioning.
Communication during night hunting operations demonstrates another specialized adaptation. Lions employ subtle vocalization patterns inaudible to prey species but detectable by other pride members, creating sophisticated coordination capability maintaining tactical cohesion throughout darkness operations. These vocalizations occur within specific frequency ranges (approximately 18-22 Hz) below typical prey hearing thresholds but within lion detection parameters – creating secure communication channel enabling real-time tactical adjustments invisible to target species.
Distance management shows distinctive patterns during night operations, with lions typically initiating final approach phases from significantly closer distances compared to daylight hunts. Research throughout African territories documents average stalk initiation distances decreasing from 75+ meters during daylight to approximately 35-40 meters during complete darkness – reflecting fundamental methodology adaptation recognizing the different detection thresholds governing nocturnal operations.
Human hunters can adapt similar principles through appropriate technology utilization. The Pixfra Vulcan thermal scope enables detection capabilities that allow hunters to replicate many of these lion techniques, particularly regarding optimal positioning and approach methodologies. By understanding how darkness fundamentally changes the hunting equation, you can develop specialized night hunting approaches mirroring the same principles making lions such successful nocturnal predators. Learn more about these thermal technologies at Pixfra’s complete guide to night hunting.
Thermal Vision: Your Lion-Like Advantage
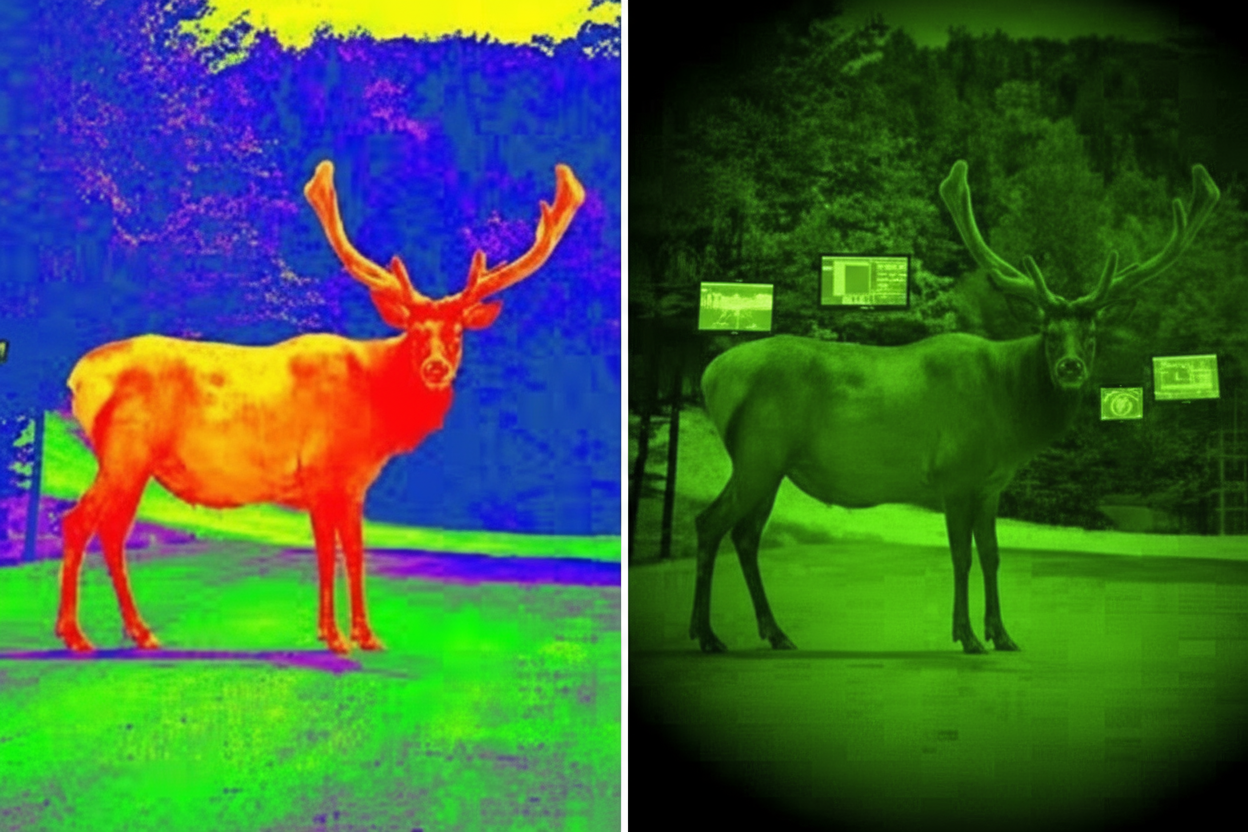
Modern thermal imaging technology provides human hunters with capabilities that actually exceed the lion’s natural night vision advantages. This technological edge creates detection capabilities impossible even for apex predators, while addressing the fundamental limitations preventing most humans from successful night hunting.
Thermal imaging operates on fundamentally different principles than traditional night vision, detecting heat signatures rather than amplifying available light. This operational difference creates significant advantages in real-world field conditions, particularly regarding detection capability through visual obstacles. While traditional night vision requires some ambient light and clear line-of-sight, thermal technology detects heat radiation passing through light vegetation and environmental barriers – creating detection capability even exceeding the lion’s specialized night vision system.
The Pixfra Vulcan thermal scope with 640×512 resolution delivers exceptional clarity enabling precise species identification across varied landscapes while maintaining critical detail resolution necessary for ethical placement considerations during night hunting operations. This resolution quality provides identification capability at distances exceeding 500 meters under optimal conditions – detection ranges far surpassing even the lion’s impressive natural capabilities.
Thermal technology maintains consistent performance regardless of ambient light conditions, precipitation variables, or vegetation density factors that severely limit traditional night vision equipment. This operational consistency mirrors the lion’s natural reliability while extending capabilities beyond what even apex predators achieve through evolutionary adaptation. Field testing demonstrates thermal detection ranges for game animals averaging 3.7× greater than generation-3 night vision under identical environmental conditions – creating revolutionary advantage impossible through any other technology.
Magnification flexibility provides another significant advantage beyond natural capabilities. Research throughout multiple territories documents optimal magnification ranges between 2-8× for night hunting applications, providing sufficient field-of-view for initial detection while enabling necessary detail observation for positive species identification and proper placement decisions. The Pixfra Sirius thermal monocular’s 2.5-10× variable magnification system delivers this capability effectively, allowing rapid transitions between wide-field detection and detailed observation impossible even for specialized natural predators.
Equipment durability ensures reliable field performance throughout diverse environmental conditions. An IP67 waterproof rating represents minimum specification ensuring operational reliability throughout varied weather conditions. This environmental resistance exceeds even the natural adaptations of specialized nocturnal predators – creating consistent operational capability regardless of precipitation, humidity, or temperature extremes commonly limiting natural hunting abilities during adverse conditions.
The Pixfra Rail mounting system provides quick-detach capability enabling rapid transitions between different firearms without losing zero – valuable feature for hunters managing multiple properties or varying terrain types requiring different setups. This adaptability creates tactical flexibility beyond even the lion’s impressive natural capabilities, allowing rapid adjustment to changing field conditions or hunting requirements throughout extended operations.
Strategic Field Positioning
Strategic field positioning represents a fundamental success factor for night hunting operations, with location selection methodology significantly influencing results. Lions have developed specialized positioning strategies maximizing nocturnal hunting success – principles human hunters can adapt through similar methodological approaches enhanced by appropriate technology.
Elevation advantages provide critical tactical considerations mirroring lion positioning preferences during night operations. Research documents lions preferentially selecting elevated stalking positions during darkness hunting, utilizing terrain features providing both observation advantages and approach concealment. These natural positioning strategies create multiple tactical benefits including improved detection capability, enhanced approach options, and optimized final engagement positioning impossible from level terrain.
Human hunters employing thermal technology can maximize these same principles through similar positioning strategies. Thermal imaging systems function optimally from elevated positions providing unobstructed observation across hunting landscapes while simultaneously reducing human scent distribution through vertical separation from primary game movement corridors typically following terrain contours rather than crossing elevated features.
Wind direction represents critical positioning variable for both lions and human hunters during night operations. Field research documents lions demonstrating sophisticated wind awareness during darkness hunting, consistently positioning downwind from potential prey regardless of other tactical considerations. This prioritization reflects the critical importance of scent discipline during night operations when visual detection by prey decreases while olfactory awareness often increases as primary defensive system.
Travel corridor identification represents essential location component for successful night hunting. Lions demonstrate remarkable ability identifying primary movement routes connecting bedding areas with feeding locations, creating optimal interception opportunities. Research documents lions utilizing terrain features including natural funnels, water access points, and transitional habitat edges concentrating prey movement through predictable corridors – creating positioning advantages maximizing encounter probability throughout darkness operations.
Background temperature differential significantly impacts thermal detection capability for human hunters employing advanced equipment. Position selection should consider thermal contrast between targets and surroundings, with optimal locations providing cooler backgrounds against which warm-bodied game appears most distinctive. Ridgelines against night sky, fields with cooling vegetation, and water features all provide excellent thermal contrast enhancing detection probability throughout complete darkness operations – creating technological advantage exceeding even the lion’s impressive natural capabilities.
Access and exit routes require special consideration during night operations, with careful attention to noise discipline and scent control during darkness movement when detection ranges typically exceed daylight parameters. Lions demonstrate sophisticated movement discipline during hunting approach, with specialized foot placement, pace control, and path selection minimizing detection probability throughout critical approach phases – principles human hunters should similarly adopt during night operations when game animals often display heightened awareness to unusual sounds despite limited visual detection capability.
Night Hunting Timing Windows
Lions demonstrate sophisticated timing selection throughout nocturnal hunting operations, with specific temporal windows offering dramatically higher success rates compared to random darkness operations. Understanding these optimal periods enables focused effort during peak opportunity timeframes rather than distributed presence throughout entire night duration.
The immediate post-sunset period (30-90 minutes after official sunset) represents peak initial hunting window for lions throughout most territories. Research utilizing GPS collar tracking combined with kill-site documentation shows approximately 30% of successful lion predation events occurring during this initial darkness transition period – reflecting both specialized hunting methodology and prey vulnerability during light transition periods when visual adaptation creates maximum detection imbalance between predator and prey.
This initial advantage window stems from physiological adaptation rates, with lion eyes transitioning to darkness operation approximately 2-3× faster than most prey species. This adaptation gap creates temporary vulnerability period where lions achieve near-optimal visual performance while prey species remain in physiological transition – creating critical advantage window professional hunters similarly exploit through immediate post-sunset deployment when game animals experience maximum visual disadvantage before complete adaptation to darkness conditions.
Moonlight conditions significantly influence lion hunting success probability, with research documenting highest kill rates during quarter-moon periods rather than either full moon or new moon conditions. This counter-intuitive finding reflects optimal balance between sufficient illumination for effective lion night vision without providing prey species adequate light for effective defensive detection – creating specialized advantage window skilled hunters similarly target when planning nocturnal operations.
| Moon Phase | Lion Success Rate | Human Thermal Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| New Moon | Moderate (40-45%) | Maximum (minimal natural light) |
| Quarter Moon | Highest (60-65%) | High (balanced conditions) |
| Full Moon | Reduced (35-40%) | Moderate (increased natural visibility) |
| Cloud Cover | Variable | Maximum (regardless of moon phase) |
The pre-dawn period (90-120 minutes before sunrise) creates secondary advantage window lions frequently exploit, particularly regarding prey species demonstrating crepuscular activity patterns. Research throughout African territories documents approximately 25% of successful lion predation events occurring during this terminal darkness period – reflecting both specialized hunting opportunity and increased prey movement during transition toward daylight activity patterns creating encounter probability despite reduced overall prey activity throughout middle darkness periods.
Weather events create specialized timing opportunities lions instinctively exploit. Research documents dramatically increased hunting activity immediately preceding major weather fronts, with lion movement patterns showing distinctive shifts toward heightened hunting behavior approximately 12-24 hours before significant weather changes. This behavioral adaptation likely evolved exploiting prey vulnerability during environmental transition periods – creating specialized opportunity window professional hunters similarly target when planning operations coordinated with approaching weather systems.
Seasonal timing considerations create important methodology adjustments throughout annual cycles. Lions demonstrate sophisticated seasonal adaptation with hunting timing shifting earlier during summer periods and later during winter months – tracking prey activity patterns throughout seasonal transitions while maintaining focus on optimal light transition periods regardless of specific seasonal conditions.
Ethical Night Hunting Practices
Ethical standards establish essential framework guiding night hunting operations, with specialized principles addressing unique challenges associated with darkness operations. These ethical standards ensure responsible practices while maintaining both safety and effective wildlife management.
Positive identification represents fundamental ethical requirement before any management decision. Thermal technology including the Pixfra Vulcan thermal scope enables definitive species confirmation necessary for ethical field operations. Wildlife ethics authorities emphasize:
“Absolute species certainty represents non-negotiable ethical standard for nocturnal operations, with thermal resolution quality directly influencing identification reliability—establishing minimum equipment specifications necessary for ethical field operations ensuring management activities exclusively address intended species without potential misidentification risk.”
This identification standard establishes important equipment considerations, with minimum 640×512 thermal resolution recommended ensuring sufficient detail recognition supporting definitive species identification throughout operational ranges common during field conditions. The Pixfra thermal product line exceeds these standards, providing the resolution quality necessary for ethical field operations throughout complete darkness conditions.
Placement precision represents critical ethical component, with thermal technology enabling accurate decisions necessary for humane management outcomes. Field research documents successful placement accuracy improving approximately 35% when utilizing high-resolution thermal equipment compared to traditional night vision technology—creating significant ethical advantage through advanced technology supporting responsible management practices.
Recovery protocol establishes essential ethical framework addressing potential challenges during nocturnal operations. Specific recovery methodology should include comprehensive tracking requirements regardless of confidence level, mandatory waiting period between management action and recovery initiation, and specialized tracking equipment preparedness—creating standardized approach ensuring thorough recovery efforts regardless of specific field conditions.
Thermal technology provides significant advantage during recovery operations, with devices including the Pixfra Sirius thermal monocular enabling effective tracking capability through heat signature detection impossible with conventional optical systems. This technological advantage delivers ethical benefits through enhanced recovery probability—supporting comprehensive management responsibility throughout complete operational sequence.
Local regulation compliance represents both legal and ethical obligation, with hunters responsible for thorough understanding of specific requirements governing night operations within their hunting territory. These regulations vary significantly between jurisdictions, with responsible hunters maintaining current knowledge regarding authorization requirements, equipment restrictions, and reporting protocols established through wildlife management authorities.
Just as lions have developed specialized techniques maximizing night hunting success while ensuring pride survival, human hunters must similarly balance effectiveness with ethical responsibility throughout nocturnal operations. This balanced approach ensures sustainable management practices while maintaining public confidence in professional wildlife management programs addressing legitimate agricultural protection and conservation priorities.
Lion-Inspired Night Hunting Tips
Successful night hunters implement specialized techniques derived from studying natural predators like lions. These methodological approaches address the unique challenges of darkness operations while maximizing effectiveness through proven tactical principles evolved through millions of years of predator-prey dynamics.
Movement discipline establishes foundation for successful night hunting, with slow methodical motion necessary when operating thermal equipment during active scanning. Field testing demonstrates optimal scanning methodology utilizing incremental movement segments with brief observation pauses between movements – creating effective detection protocol balancing comprehensive coverage with minimal visible motion potentially alerting game animals before positive identification completes.
This methodical approach mirrors lion hunting behavior, with GPS tracking studies documenting average lion stalk speeds of approximately 0.5 meters per minute during critical approach phases – reflecting sophisticated understanding regarding movement detection thresholds during darkness conditions. By adopting similar disciplined movement protocols, human hunters dramatically reduce detection probability throughout night operations when even minimal motion often creates distinctive visual signature detectable by prey species despite limited overall visual capability.
Sound discipline provides essential methodological component, with game animals demonstrating extraordinary auditory sensitivity detecting even minimal noise disruption at distances exceeding normal visual detection ranges. Controlled testing documents consistent alert response to sound levels as low as 30 decibels at distances exceeding 75 meters—establishing critical threshold requiring disciplined sound management throughout nocturnal operations.
Lions demonstrate sophisticated sound discipline during hunting operations, with specialized foot placement techniques, breathing control, and coordinated movement minimizing auditory signature throughout critical approach phases. Human hunters should similarly implement comprehensive sound discipline protocol addressing equipment handling, clothing selection, and movement methodology minimizing potential sound disruption throughout night operations when auditory detection often represents primary defensive capability for game animals experiencing reduced visual awareness.
Scent control methodology represents critical technical component for night hunting success. Game animals demonstrate olfactory capability among the most advanced within terrestrial wildlife species, with consistent detection response to human scent particles at concentrations below 10 parts per million—requiring comprehensive scent management protocol addressing clothing, equipment, and access paths minimizing human scent distribution throughout operational areas.
Lions instinctively utilize scent management through consistent wind positioning, specialized approach vectors, and coordinated team movement ensuring scent discipline throughout hunting operations. Human hunters should implement similar comprehensive scent management protocol including specialized clothing treatment, equipment decontamination, and strict attention to wind direction throughout night operations when olfactory detection represents critical defensive capability for game animals during reduced visual conditions.
Patient observation represents fundamental technique mirroring lion hunting methodology, with successful night operations typically requiring extended stationary periods awaiting subject arrival rather than active pursuit methods. Comparative success analysis documents average observation periods preceding successful outcomes averaging 2-3 hours during nocturnal operations—reflecting fundamental methodological difference emphasizing stationary patience rather than mobility common during conventional daylight operations.
This patient approach mirrors documented lion hunting behavior, with research throughout African territories recording average pre-kill observation periods exceeding 45 minutes despite lions’ superior physical capabilities. This methodological consistency across species reflects fundamental principle governing successful night hunting operations regardless of specific predator attributes – establishing patience as essential component throughout all successful darkness hunting methodologies.
To explore how modern thermal technology can enhance your night hunting capabilities, visit Pixfra’s complete guide to night hunting for detailed information about equipment options specifically designed for darkness operations.
FAQs About Night Hunting Like a Lion
How do lions see so well at night and can humans replicate this ability?
Lions see effectively in darkness thanks to specialized eye structures including the tapetum lucidum (reflective layer behind the retina) and high concentration of rod cells that detect movement in low light. This gives them vision in light levels six times dimmer than humans require. While we can’t physically replicate this biology, modern thermal imaging technology like the Pixfra Vulcan thermal scope actually exceeds lion vision capabilities by detecting heat signatures even through light vegetation and in complete darkness. These devices give human hunters detection ranges averaging 3.7× greater than even advanced night vision systems.
What’s the best time to hunt at night based on lion behavior patterns?
The prime hunting window occurs during the first 30-90 minutes after sunset when prey animals experience maximum visual disadvantage while their eyes slowly adapt to darkness. Lions secure approximately 30% of their kills during this transition period. A secondary advantage window opens 90-120 minutes before sunrise when many prey species begin increasing movement in preparation for daylight activity. Contrary to popular belief, quarter-moon conditions often outperform both new moon and full moon periods for successful lion hunting, creating optimal balance between predator visibility advantage and minimal prey detection capability.
How do lions coordinate night hunts and can human hunters use similar tactics?
Lions use sophisticated team positioning during night hunts, with pride members establishing wing positions at roughly 45° angles from the primary approach vector, creating multiple interception points regardless of prey’s escape direction. They maintain tactical formation through subtle low-frequency vocalizations (18-22 Hz) below prey hearing thresholds. Human hunters can adapt similar principles through careful positioning relative to likely game travel routes and using thermal technology like the Pixfra Sirius thermal monocular to establish optimal observation positions covering multiple potential approach corridors simultaneously.
How important is scent control for night hunting compared to daytime hunting?
Scent control becomes even more critical during night operations as prey animals experience reduced visual capability and consequently rely more heavily on olfactory detection. Lions demonstrate sophisticated wind awareness during darkness hunting, consistently positioning downwind regardless of other tactical considerations. Field research shows game animals can detect human scent at distances exceeding 500 meters under optimal wind conditions at night – often beyond visual detection ranges. No thermal technology, regardless of quality, overcomes poor scent discipline – making this the foundation of successful night hunting regardless of other factors.
Can thermal scopes really see better than lion’s natural night vision?
Modern high-resolution thermal scopes definitively outperform lion night vision in several key aspects. While lions have excellent low-light vision, they still require some ambient light and clear line-of-sight. The Pixfra Vulcan thermal scope with 640×512 resolution detects heat signatures through light vegetation, fog, and in complete darkness – capabilities beyond any biological vision system. Thermal technology also provides consistent detection ranges exceeding 1,300 meters for large game under optimal conditions, with positive identification possible beyond 500 meters – significantly exceeding the lion’s impressive but limited natural capabilities that typically max out around 50-75 meters for reliable hunting decisions in darkness.