When it comes to protecting your property, assets, or critical infrastructure, traditional security cameras can only do so much. That’s where thermal detection technology steps in, offering a whole new level of protection that works around the clock—no matter the weather, lighting, or visibility conditions. We’ve seen how this tech has changed the game for businesses, construction sites, and industrial facilities across the country.
Thermal detection systems use heat signatures instead of visible light to spot threats, intruders, fires, and equipment failures before they become real problems. Whether you’re monitoring a large perimeter, securing equipment at night, or trying to prevent fires on a job site, thermal cameras give you eyes that never sleep. They can see through darkness, fog, smoke, and even detect people hiding in bushes or behind obstacles. Plus, they cut down on false alarms that come from shadows, moving branches, or small animals—things that often trigger regular cameras.
If you’re into outdoor activities and want to see how thermal tech works in action, check out our guide on fox hunting at night, where we show you how thermal imaging helps spot wildlife in total darkness. At Pixfra, we’re all about using cutting-edge tech to help you see what others can’t, whether that’s for security, outdoor adventures, or professional applications.
How Thermal Detection Systems Work
Thermal detection systems operate on a completely different principle than your standard security cameras. Instead of capturing visible light, these systems detect infrared radiation—basically the heat that every object gives off based on its temperature. Every person, vehicle, animal, and piece of equipment emits heat, and thermal cameras pick up on those heat signatures to create visual images.
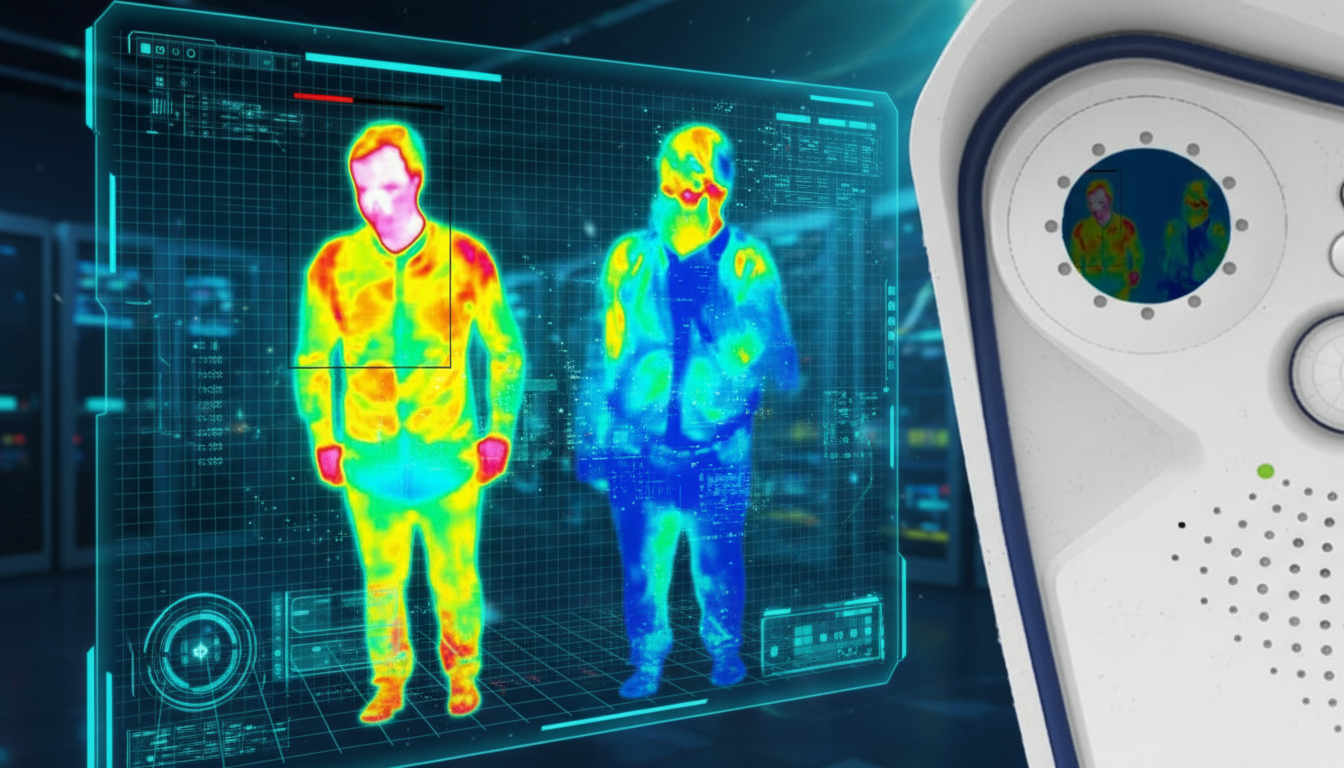
The core component is an infrared sensor that measures the temperature differences in a scene. These sensors convert thermal energy into electronic signals, which then get processed to display a thermal image. Warmer objects show up as bright spots (usually in white, red, or yellow), while cooler objects appear darker (in blues, greens, or black). This lets you spot a person’s body heat against a cool background, or detect overheating machinery in an industrial setting.
What makes this tech so powerful for security is that it doesn’t need any light to work. Traditional cameras struggle when it gets dark or when there’s glare, shadows, or bad weather. Thermal cameras don’t care about any of that—they work just as well at 3 AM in the rain as they do at noon on a sunny day. They can see through fog, smoke, light foliage, and even some types of plastic or fabric that would block regular cameras.
Thermal Perimeter Detection
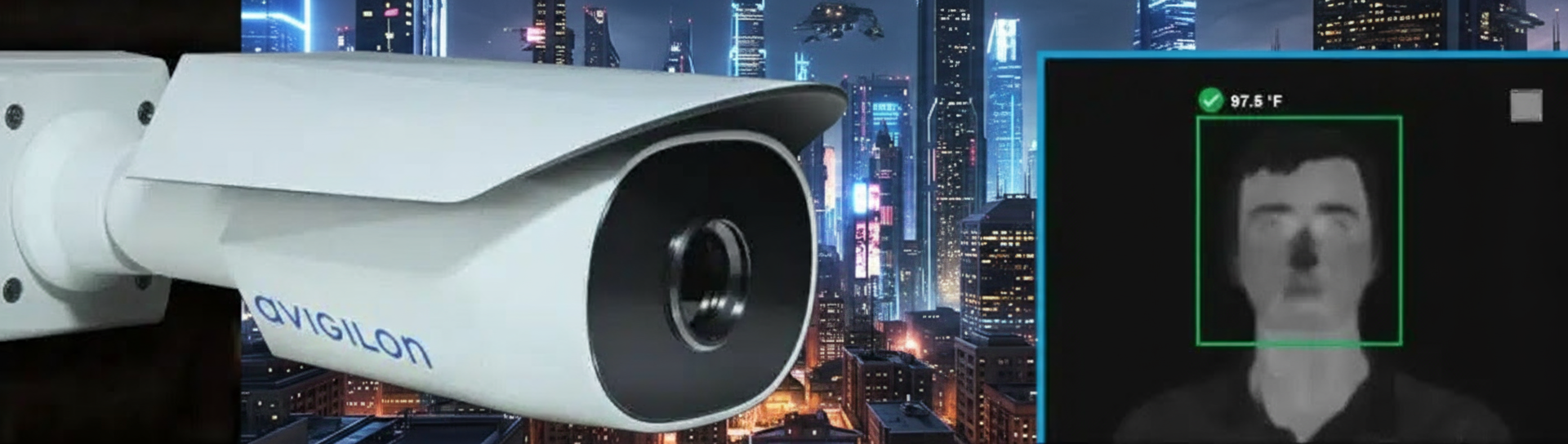
One of the biggest applications for thermal detection in security is perimeter protection. Businesses, industrial sites, utilities facilities, and warehouses all need to know if someone’s trying to get in where they shouldn’t be. Thermal cameras excel at monitoring long fence lines, property boundaries, and open areas where traditional cameras would need tons of lighting or would miss intruders in the dark.
Thermal sensors can detect a person’s heat signature from hundreds of feet away—some high-end models can spot threats over 1,000 feet out. That means fewer cameras to cover the same area, which saves on installation and maintenance costs. When someone crosses into a restricted zone, the system can trigger an alert and even steer a PTZ camera to zoom in and capture detailed visual footage for verification.
What really sets thermal perimeter detection apart is how well it handles environmental challenges. Rain, snow, fog, and darkness don’t affect thermal imaging the way they mess with traditional cameras. The systems can operate reliably in extreme temperatures, from -40°F to over 138°F, making them perfect for outdoor security in any climate. Plus, when you combine thermal cameras with smart analytics, they can tell the difference between a person, a vehicle, and an animal—cutting down on those annoying false alarms that come from deer or raccoons wandering past your fence.
Detection in Complete Darkness
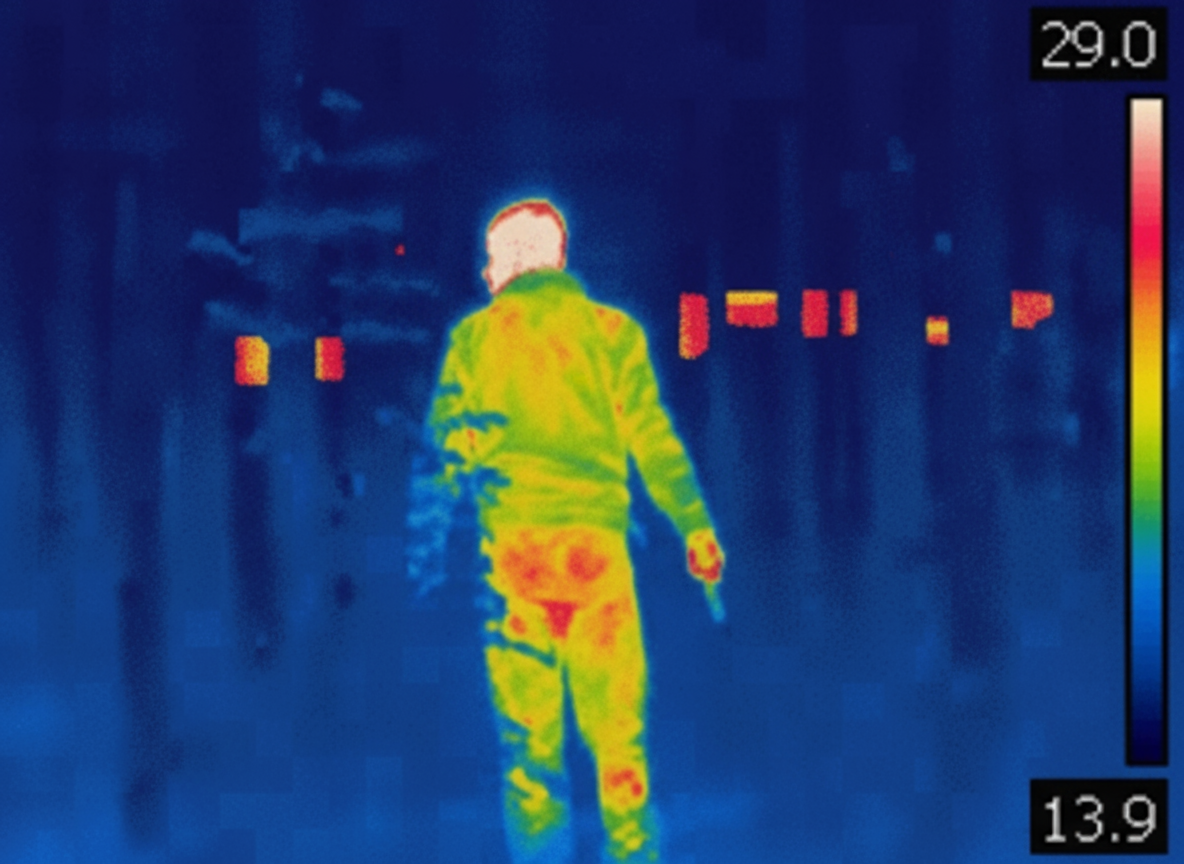
Let’s talk about one of the most powerful benefits of thermal detection: its ability to work in total darkness. Traditional security cameras need some kind of light source—whether that’s streetlights, building lights, or infrared illuminators—to capture useful footage. When the lights go out, those cameras struggle, producing grainy, unclear images that make it hard to identify threats.
Thermal cameras flip that problem on its head. They detect heat, not light, which means they work perfectly in zero-light conditions. A person walking across your property at 2 AM shows up just as clearly as they would at noon. This makes thermal detection ideal for securing areas where lighting is limited, impractical, or just not possible—like remote perimeters, construction sites after hours, rooftops, or rural facilities.
Here’s what thermal detection can do in darkness:
- Spot intruders in complete blackout conditions
- Detect people trying to hide in shadows or behind obstacles
- Monitor large outdoor areas without expensive lighting infrastructure
- Identify threats even when they’re wearing dark clothing or camouflage
This 24/7 detection capability is a huge deal for businesses that need constant surveillance but don’t want to light up their entire property all night. It saves energy costs and reduces light pollution while still keeping your site secure. Plus, since thermal cameras don’t rely on visible light, intruders have no idea they’re being watched—there’s no telltale glow from infrared LEDs to tip them off.
Reducing False Alarms with Thermal Technology
Anyone who’s dealt with traditional motion-detection security systems knows the headache of false alarms. A tree branch swaying in the wind, a stray cat, headlights from a passing car, or shifting shadows can all trigger alerts. When your security team gets bombarded with false alarms day after day, they start ignoring them—which defeats the whole purpose of having a security system.
Thermal cameras cut through that noise. Because they detect heat signatures instead of just motion, they’re way better at filtering out non-threatening activity. A branch blowing in the wind doesn’t give off heat, so it won’t trigger an alarm. Same goes for shadows moving across the ground or leaves rustling in the breeze. When you add intelligent analytics to the mix, thermal systems can classify detected objects as humans, vehicles, or animals based on their heat patterns and size.
This classification ability means you can set your system to only alert you about real threats. If a deer wanders past your fence, the system recognizes it’s an animal and doesn’t send an alert. But if a person approaches, you get notified immediately. This reduces false alarms by a huge margin—some systems report accuracy rates of 99% or higher when thermal cameras work together with smart analytics.
The result? Your security team can focus on actual threats instead of chasing down every squirrel that crosses the yard. That means faster response times when real incidents happen, less wasted time investigating false alerts, and overall better security coverage. Plus, when you do get an alarm, you can trust that it’s something worth checking out.
Fire Detection and Temperature Monitoring
Beyond spotting intruders, thermal detection plays a huge role in fire prevention and equipment monitoring. Thermal cameras can measure the temperature of objects in their field of view, making them perfect for detecting hot spots before they turn into full-blown fires. This is especially valuable in industries where fire risk is high—like scrap yards, recycling centers, lumber yards, and industrial facilities.
Here’s how it works: you set temperature thresholds for specific areas or equipment. When the thermal camera detects that something has crossed that threshold—maybe a piece of machinery is overheating, or there’s a hot spot building in a pile of materials—it sends an alert. This gives you time to investigate and take action before smoke or flames appear. In many cases, thermal detection can spot fires in their earliest stages, when they’re still smoldering and haven’t produced visible smoke yet.
Thermal cameras are also fantastic for monitoring electrical systems. Overheating connections, failing components, and electrical faults all produce heat before they fail completely. Regular thermal inspections can identify these issues early, allowing for preventive maintenance that stops equipment breakdowns, reduces downtime, and prevents potential fire hazards. This makes thermal detection a dual-purpose tool that enhances both safety and security at the same time.
For construction sites, thermal detection offers another layer of protection. Sites often have valuable equipment, materials, and work-in-progress that need monitoring after hours. Thermal cameras can detect unauthorized people entering the site at night while also watching for fire risks from welding equipment, electrical work, or other heat sources that might pose a danger.
The Top Six Reasons for Using Thermal Security Cameras
When you’re evaluating whether thermal detection makes sense for your security needs, it helps to break down the specific advantages. Based on what we’ve learned from industry experts and real-world applications, here are the top reasons businesses invest in thermal security cameras:
1. All-Weather, All-Conditions Performance – Thermal cameras work reliably in rain, snow, fog, smoke, and dust. They’re not affected by glare from the sun or blinding from headlights, and they don’t care about lighting conditions at all.
2. Long-Range Detection – Quality thermal cameras can detect heat signatures at extreme distances, often 3-5 times farther than visible cameras can see clearly. This means fewer cameras to cover large areas, which reduces costs.
3. Fewer False Alarms – By detecting heat instead of motion, and with smart analytics that classify objects, thermal systems dramatically reduce false alarms from environmental factors, animals, and weather.
4. Privacy-Friendly Monitoring – Thermal images don’t show facial features or identifying details, making them ideal for applications where privacy regulations are strict. You can detect presence without capturing personal information.
5. Dual-Purpose Security and Safety – The same cameras that detect intruders can also monitor for fire hazards, overheating equipment, and temperature anomalies that could signal problems.
6. 24/7 Uninterrupted Surveillance – Thermal detection never stops working, regardless of time of day or lighting conditions. You get constant, reliable monitoring without gaps in coverage.
These benefits add up to create a security solution that’s more reliable, more cost-effective, and more versatile than traditional camera systems. When you factor in the reduced false alarms, longer detection ranges, and all-weather operation, thermal cameras often deliver a better return on investment despite their higher upfront cost.
Common Applications and Industries
Thermal detection technology has found its way into a wide range of security applications across different industries. Let’s look at where this tech makes the biggest impact:
Construction Sites – After-hours monitoring is a huge challenge for construction sites. Thermal cameras detect people entering when no one should be there, helping prevent theft of equipment, materials, and tools. They also monitor for fire hazards from electrical work or hot equipment.
Industrial Facilities and Warehouses – These sites often have outdoor storage areas, equipment yards, and perimeters that need monitoring. Thermal detection provides reliable security for outdoor assets while also watching for equipment overheating and fire risks.
Critical Infrastructure – Power plants, utilities facilities, water treatment plants, and data centers use thermal detection to protect vital assets and monitor for both security threats and equipment failures. The ability to detect intruders and overheating equipment with the same system is a major plus.
Retail and Commercial Properties – Parking lots, loading docks, and the backs of stores are common targets for theft and vandalism. Thermal cameras monitor these areas effectively at night without requiring expensive lighting.
Airports and Transportation Hubs – Large perimeters and areas that need constant surveillance benefit from thermal detection’s long-range capabilities and all-weather performance.
Government and Military Sites – High-security locations use thermal detection for perimeter protection, especially in areas where visibility is limited or where the perimeter is too large for traditional cameras.
Each of these applications takes advantage of thermal detection’s unique strengths—working in darkness, seeing through weather, detecting at long range, and reducing false alarms. The technology adapts to different needs based on the specific challenges each industry faces.
FAQs
How far can thermal security cameras detect intruders?
Thermal security cameras can detect heat signatures from hundreds to over 1,000 feet away, depending on the camera’s resolution, lens, and sensor quality. High-end models designed for perimeter security can spot a person at distances over 300 meters (about 984 feet), while some specialized long-range systems can detect threats even farther. Detection range also depends on the size of the object—larger heat sources like vehicles can be detected from greater distances than individual people.
Do thermal cameras work in extreme weather conditions?
Yes, thermal cameras work exceptionally well in extreme weather. They can operate in temperatures ranging from -40°F to over 138°F and aren’t affected by rain, snow, fog, or dust. Unlike traditional cameras that struggle when weather blocks visibility, thermal cameras see through these conditions by detecting heat signatures. This makes them ideal for outdoor security applications in any climate, from harsh winters to hot summers.
Can thermal detection systems integrate with existing security infrastructure?
Most modern thermal detection systems are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing security setups. They work with standard video management systems (VMS), can connect to alarm systems, and often include ONVIF compliance for compatibility with third-party equipment. Many thermal cameras can also work alongside traditional visible-light cameras, with analytics that automatically steer PTZ cameras to zoom in on thermal detections for detailed visual verification.
Are thermal security cameras worth the investment for small businesses?
While thermal cameras have a higher upfront cost than traditional cameras, they can deliver excellent value for small businesses with specific security challenges. If you need to monitor outdoor areas at night, have issues with false alarms, or need to cover large perimeters with fewer cameras, thermal detection can save money in the long run. The reduced false alarms mean less wasted time for security staff, and the longer detection range means you need fewer cameras overall.
What’s the difference between thermal cameras and night vision for security?
Thermal cameras detect heat signatures and work in total darkness without any light source, creating images based on temperature differences. Night vision cameras amplify existing light (or use infrared illuminators) to create visible images, so they need at least some light to function effectively. Thermal cameras work better in complete darkness, through smoke and fog, and can detect hidden threats based on heat. Night vision provides more detailed images with better resolution when there’s at least minimal light available. For security applications where 24/7 monitoring in all conditions is needed, thermal detection is usually the better choice.